
ARTICLES /
Difference between Incorporated and Unincorporated Joint Venture
JULY 2024
Incorporated JV
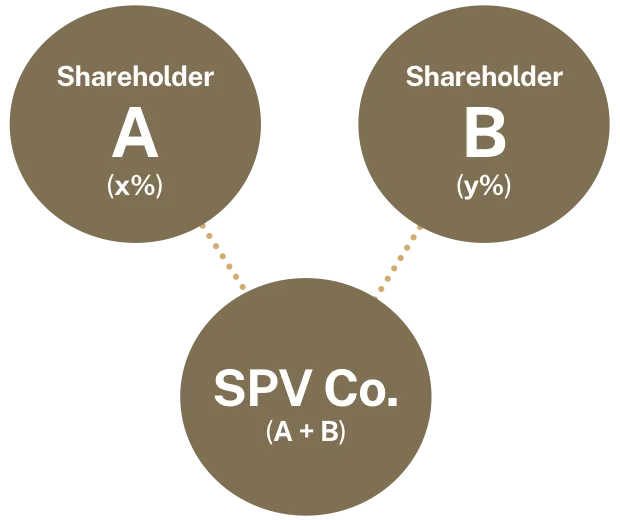
An incorporated joint venture is a separate legal entity (or known as a special purpose vehicle) formed by two or more parties.
Unincorporated JV
An unincorporated joint venture is an arrangement between two or more parties to collaborate without forming a separate legal entity.

Features
An Incorporated JV typically involves:
- Formation of Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
- Entering into a Joint Venture & Shareholders’ Agreement
- Capital Contribution to the SPV
- The parties become shareholders in the SPV, who may appoint directors of the SPV
- Control/ Participation in SPV
- Sharing of profits and losses generated by the SPV
Terms to Consider
(Non-exhaustive)
- Capital contribution by each party
- Shareholders’ equity proportions
- Directorship (Number of Directors, Quorum requirements, Approvals)
- Reserved Matters (Requiring unanimous approval from all shareholders)
- Deadlock Resolution
- Exit Strategy
Features
An Incorporated JV typically involves:
- Formation of Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
- Entering into a Joint Venture & Shareholders’ Agreement
- Capital Contribution to the SPV
- The parties become shareholders in the SPV, who may appoint directors of the SPV
- Control/ Participation in SPV
- Sharing of profits and losses generated by the SPV
Terms to Consider
(Non-exhaustive)
- Scope of joint venture or collaboration
- Roles and responsibilities of each party
- Contributions and control of Funds
- Profit and Loss Sharing
- Decision Making Process
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- Termination and Consequences
- Liability and Indemnification